What Neurons Does Parkinsons Affect: Unveiling The Brains Role
Parkinson’S Disease: How Is The Brain Affected?
Keywords searched by users: What neurons does Parkinson’s affect Parkinson’s disease, Parkinson’s disease là gì, degeneration of dopaminergic neurons causes which disease, what causes the death of dopaminergic neurons in parkinson’s disease, role of dopamine in parkinson’s disease, parkinson’s disease organs affected, Stage of parkinson’s disease, in parkinson’s disease, which pathway in the brain degenerates?
What Type Of Neurons Are Lost In Parkinson’S Disease?
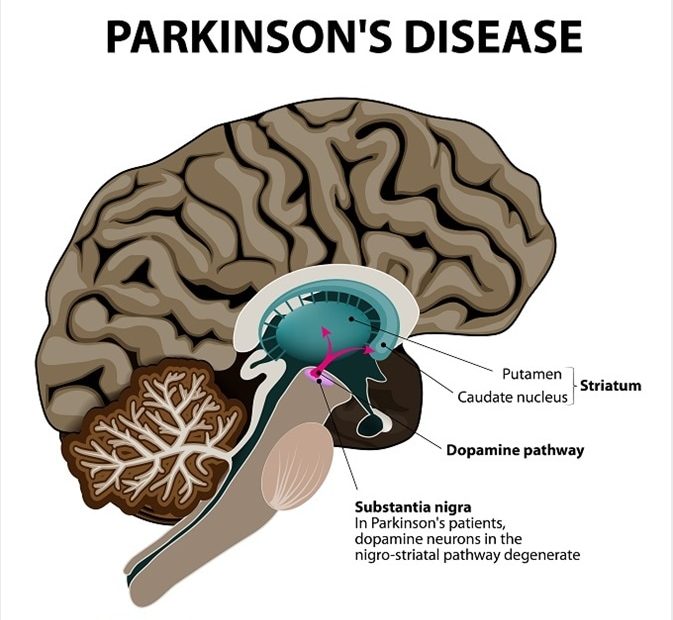
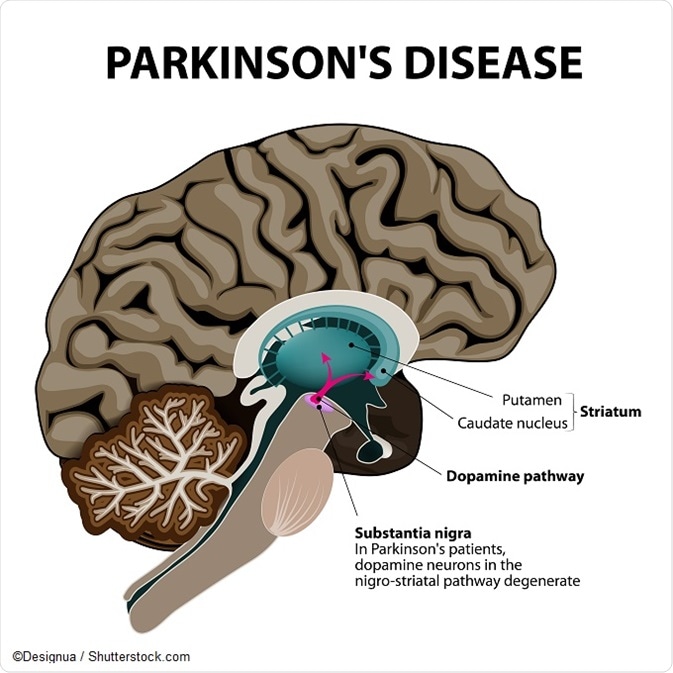
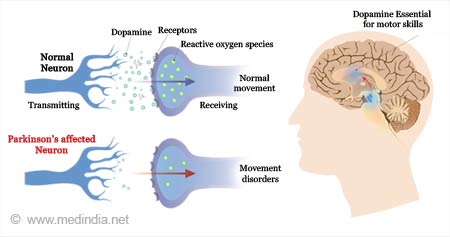
Parkinson’s disease is characterized by the degeneration of a specific type of neurons known as dopamine-producing neurons. These neurons are primarily located in a critical area of the midbrain called the substantia nigra. This loss of dopamine-producing neurons is a central feature of the disease and leads to a deficiency of dopamine, a neurotransmitter responsible for regulating movement and coordination. This deficit in dopamine function is what gives rise to the characteristic motor symptoms associated with Parkinson’s disease, such as tremors, rigidity, and bradykinesia (slowness of movement). This neurological condition profoundly affects a person’s ability to control their movements and can have a significant impact on their overall quality of life.
What Part Of The Neuron Is Affected By Parkinson’S Disease?
Parkinson’s disease (PD) is a neurodegenerative disorder that primarily impacts a particular type of brain cell known as dopamine-producing neurons. These neurons are located within a specific region called the substantia nigra. When someone has Parkinson’s disease, these dopaminergic neurons in the substantia nigra experience degeneration, leading to the characteristic motor symptoms associated with the condition. These symptoms include tremors, stiffness, and difficulty with movement due to the reduced production of dopamine, a neurotransmitter crucial for motor control.
Does Parkinson’S Affect Motor Neurons?
Is Parkinson’s disease associated with the impairment of motor neurons? The impact of sporadic Parkinson’s disease on motor units, as assessed through the multipoint incremental Motor Unit Number Estimation (MUNE) method, is indeed indicative of lower motor neuron involvement. However, it’s important to note that the loss of motor neurons is relatively mild and doesn’t occur uniformly across all muscle groups. This variation in motor neuron loss among different muscles is a notable characteristic of the condition.
Collect 29 What neurons does Parkinson’s affect
Categories: Summary 32 What Neurons Does Parkinson’S Affect
See more here: trainghiemtienich.com

Parkinson’s disease (PD) is a degenerative, progressive disorder that affects nerve cells in deep parts of the brain called the basal ganglia and the substantia nigra. Nerve cells in the substantia nigra produce the neurotransmitter dopamine and are responsible for relaying messages that plan and control body movement.Parkinson’s disease is marked by the death of dopamine-producing neurons in the brain — specifically in the substantia nigra, a structure deep within a region of the brain called the midbrain.Parkinson’s disease (PD)
A neurodegenerative disorder that affects predominately the dopamine-producing (“dopaminergic”) neurons in a specific area of the brain called substantia nigra.
Learn more about the topic What neurons does Parkinson’s affect.
- Parkinson’s disease (PD) – Mayfield Clinic
- Why a specific type of neuron dies in Parkinson’s disease | Broad Institute
- What is Parkinson’s?
- Motor neurons loss in Parkinson Disease – ScienceDirect.com
- Neuronal Cell Death in Alzheimer’s Disease and a Neuroprotective …
- α-Synucleinopathy and selective dopaminergic neuron loss in a rat …