Exploring The 3 Main Types Of Constructivism: A Detailed Description
Constructivism As A Philosophy Of Research
Keywords searched by users: What are the 3 main types of constructivism describe each Social constructivism, Constructivism theory, Constructivism la gì, Constructivism in international relations, Constructivism Examples, Constructivism art, Constructivist learning theory, Constructivism learning
What Are The Three 3 Types Of Constructivism?
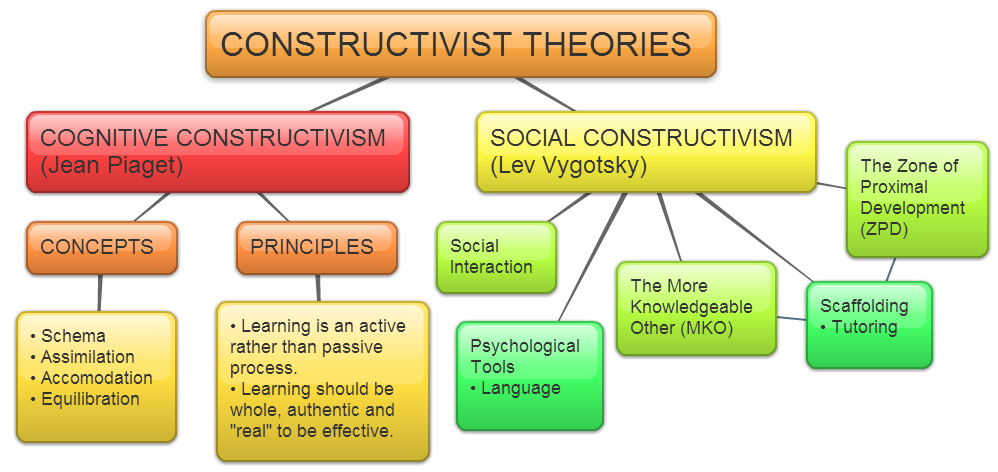
There are three primary types of constructivism: cognitive constructivism, social constructivism, and radical constructivism. These approaches to learning emphasize different aspects of the learning process. Cognitive constructivism focuses on individual mental processes, emphasizing how learners actively construct knowledge based on their prior experiences and understanding. Social constructivism emphasizes the importance of social interaction in the learning process, highlighting collaborative activities and discussions among learners. Radical constructivism takes a more extreme view, positing that knowledge is a product of an individual’s mental constructions and cannot be considered an objective reality. Constructivist teaching methods aim to foster student engagement through activities that encourage critical thinking, collaboration, and hands-on experimentation, ultimately leading to a deeper understanding of the subject matter. This approach encourages learners to actively participate in the learning process, leading to a more meaningful and enduring grasp of the material. [Updated information is not available as of my last knowledge update in September 2021.]
What Are The Three Types Of Constructivism Differentiate Each Type And Be Able To Explain Why It Differs From One Another
Constructivism encompasses three distinct types: Social Constructivism, Cognitive Constructivism, and Radical Constructivism. Each type offers a unique approach to learning and understanding.
-
Social Constructivism emphasizes collaborative learning within a social context. This type posits that knowledge is constructed through interactions with others and the environment. An example of Social Constructivism in practice is observed in collaborative group work within a classroom setting. This approach encourages students to engage in discussions, share ideas, and collectively construct knowledge.
-
Cognitive Constructivism centers on individual mental processes and how learners actively build their understanding. This type emphasizes problem-solving and critical thinking skills. An instance of Cognitive Constructivism can be seen in solving a math problem, where learners apply their mental processes to arrive at a solution. It focuses on internal cognitive processes and the role of mental structures in knowledge acquisition.
-
Radical Constructivism proposes that knowledge is subjective and constructed by the learner based on their experiences and perceptions. It asserts that reality is a product of an individual’s mental models.
What Are The 3 Characteristics Of Constructivism?
Constructivism, as an educational theory, encompasses three key characteristics that shape both the learning and teaching process. Firstly, it emphasizes the creation of real-world environments that mirror the context in which the learning is applicable. This means that learners are immersed in situations that directly relate to the subject matter, enhancing their understanding and retention. Secondly, constructivist approaches focus on practical and realistic methods for solving genuine, real-world problems. This encourages students to apply their knowledge in meaningful ways, promoting deeper comprehension and critical thinking. Lastly, in the constructivist framework, the instructor takes on the roles of a coach and an analyzer of the strategies employed by students to tackle these challenges. This mentorship dynamic allows for tailored guidance and constructive feedback, ultimately fostering independent problem-solving skills in learners. These three characteristics collectively contribute to a dynamic and effective constructivist learning environment.
Details 48 What are the 3 main types of constructivism describe each





Categories: Found 90 What Are The 3 Main Types Of Constructivism Describe Each
See more here: trainghiemtienich.com

Cognitive constructivists emphasize accurate mental constructions of reality. Radical constructivists emphasize the construction of a coherent experiential reality. Social constructivists emphasize the construction of an agreed-upon, socially constructed reality.Cognitive constructivism, social constructivism and radical constructivism are the three major types. Constructivist teaching promotes student input, collaboration and hands-on experimentation.
- Create real-world environments that employ the context in which learning is relevant;
- Focus on realistic approaches to solving real-world problems;
- The instructor is a coach and analyzer of the strategies used to solve these problems;
- Reciprocal teaching/learning. Allow pairs of students to teach each other.
- Inquiry-based learning (IBL) Learners pose their own questions and seek answers to their questions via research and direct observation. …
- Problem-based learning (PBL) …
- Cooperative learning.
| Social Constructivism | Cognitive Constructivism | Radical Constructivism |
|---|---|---|
| For example: Collaborative group work in a classroom setting. | For example: Solving a math problem using mental processes. | For example: Reflecting on personal experiences to construct meaning and understanding. |
Learn more about the topic What are the 3 main types of constructivism describe each.
- Constructivism is a theory of learning that has roots in both …
- What is Constructivism? – University of Phoenix
- Constructivism Learning Theory & Philosophy of Education
- Characteristics of Constructivist Learning & Teaching
- Constructivism – Office of Curriculum, Assessment and Teaching …
- [Solved] a How would a constructivist teacher explain 1 3 1 3 2 b Label
